Metric sort II radio bursts are a sort of photo voltaic radio emission characterised by a slowly drifting radio emission noticed in dynamic spectra. They’re generated by the interplay of a coronal shock wave with the ambient photo voltaic wind plasma.
We current our latest research, the place we’ve got compiled a complete catalog of metric sort II radio bursts utilizing information from the Radio Photo voltaic Telescope Community (RSTN). This research provides the prevalence, associations, and properties of radio emissions and their mother or father photo voltaic exercise phenomena.
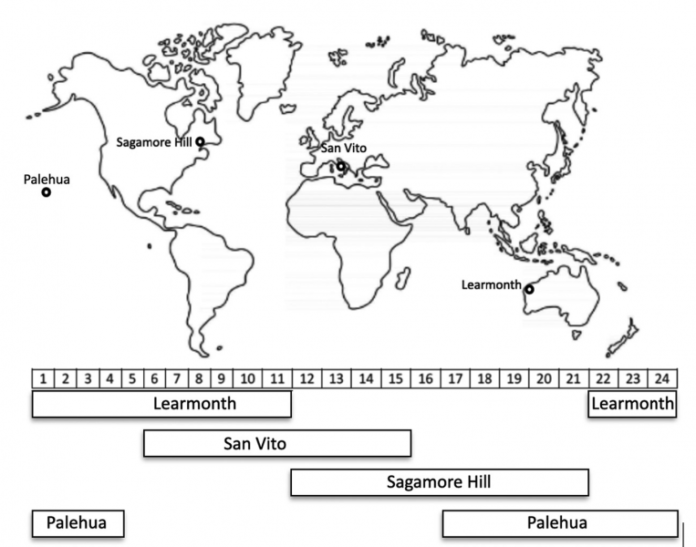
Our staff has rigorously categorized the m-type II radio bursts into two distinct qualitative teams: sure and unsure, based mostly on the depth and readability of the radio emission options. Analyzing information from Photo voltaic Cycle 24 (2009 – 2019), obtainable from RSTN stations at Learmonth, Sanvito, Sagamore Hills, and Palehua, we’ve got recognized all metric sort II bursts (429) detected throughout the 25 – 180 MHz vary via thorough visible inspection.
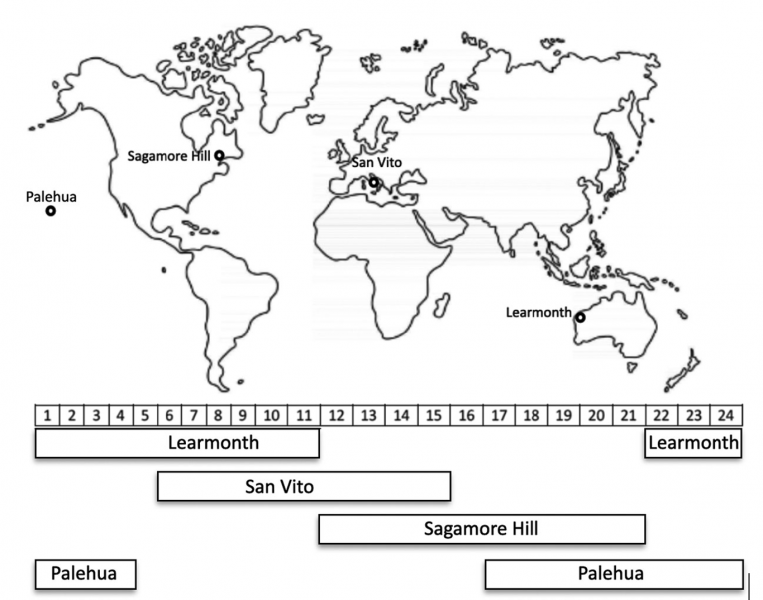
Determine 1 The situation of the 4 RSTN stations on the world map and their time of remark given in Common Time (proven beneath the world map).
We have now explored the relationships between the radio bursts and photo voltaic eruptive occasions like photo voltaic flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). Our research presents and discusses these connections, providing priceless insights into photo voltaic and space-weather actions from a ground-based radio perspective.
The newly assembled catalog of metric sort II bursts and their related photo voltaic occasions is a priceless useful resource for the photo voltaic scientific neighborhood, and is freely obtainable on-line: https://catalogs.astro.bas.bg/
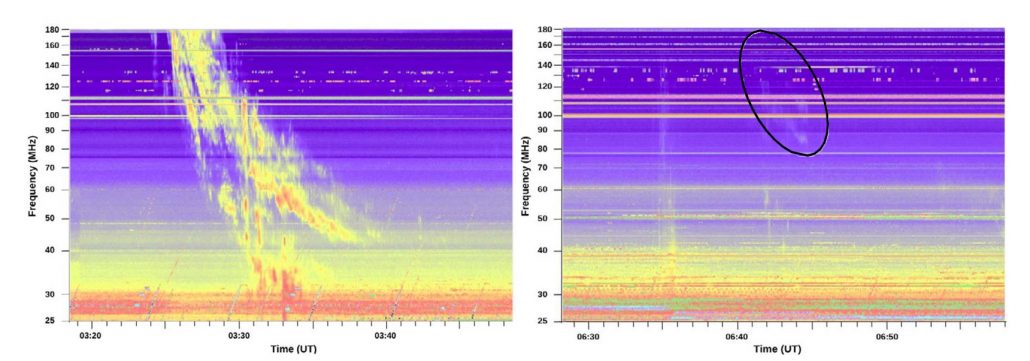
Determine 2 Examples of m-type II radio bursts for sure (left) and unsure (proper) occasions on 04 November 2015 and 02 March 2015, respectively. The spectra are chosen from the Learmonth Hill station of the RSTN community. The faint m-type II radio bursts within the unsure case are enclosed contained in the black oval.
We recognized 17% (out of 429) new bursts and located that 61% are short-lived, underneath quarter-hour. The temporal offsets between bursts and photo voltaic occasions assorted, with sure bursts being extra widespread and related to stronger photo voltaic eruptions.
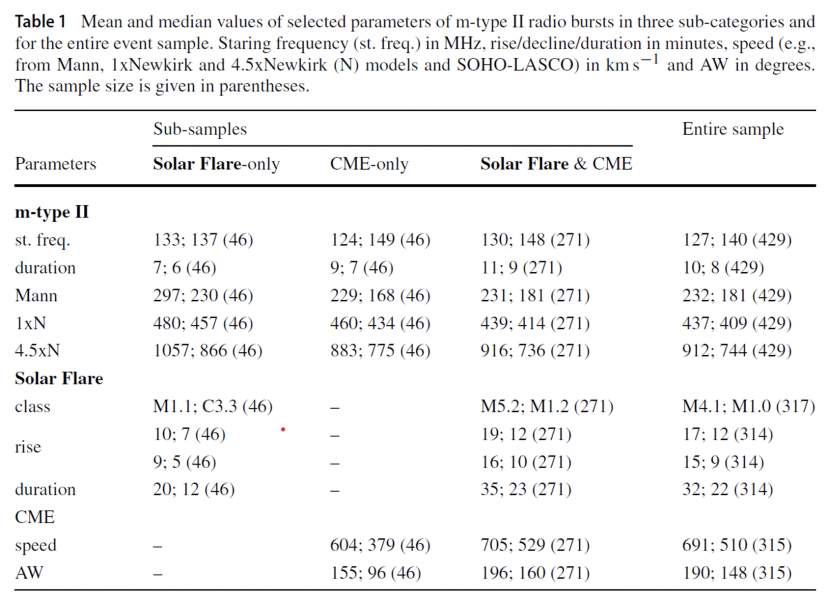
This research has developed a complete catalog of m-type II radio bursts from Photo voltaic Cycle 24, using information from the RSTN. The catalog contains 429 occasions, and the photo voltaic actions associated to those bursts, equivalent to photo voltaic flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), have been investigated. The principle findings of the research are as follows:
- New Identifications: 17% (74 out of 429) of the m-type II bursts have been new identifications made after a cautious visible inspection of the RSTN dynamic spectra.
- Prevalence Traits: The occurrences of m-type II bursts, together with their mother or father photo voltaic flares and CMEs, comply with the photo voltaic cycle pattern. About 61% (261 out of 429) of those occasions are comparatively short-lived, lasting underneath quarter-hour.
- Affiliation with Photo voltaic Flares: 74% (318 out of 429) of the m-type II bursts are related to photo voltaic flares. Most of those flares are labeled as M and C class based mostly on their GOES SXR depth. The rise instances of those flare-associated bursts are usually between 6 and 10 minutes. The lively area belts associated to those occasions are located across the photo voltaic equator with no vital hemispheric asymmetry.
- Affiliation with CMEs: 73% (315 out of 429) of the m-type II bursts are related to CMEs. About half (49%) of those CMEs have speeds lower than 500 km/s, and solely one-third are halo CMEs.
- Velocity Calculations: The pace of the m-type II bursts was calculated utilizing three completely different density fashions. There was no vital correlation between the speeds of CMEs and m-type II bursts, though quick CMEs typically are usually related to quick shock drivers.
- Photo voltaic Drivers: m-type II bursts related to solely photo voltaic flares or solely CMEs every account for about 10% of the instances. The vast majority of the occasions (63%) contain each photo voltaic flares and CMEs. When each photo voltaic drivers are current, the related m-type II bursts are inclined to have longer durations and are accompanied by stronger and sooner photo voltaic eruptions. Nevertheless, the deduced shock speeds are intermediate in worth.
These findings present priceless insights into the traits and drivers of m-type II radio bursts throughout Photo voltaic Cycle 24.
Based mostly on a latest paper: Bendict Lawrance, Pooja Devi, Ramesh Chandra, Rositsa Miteva A Catalog of Metric Sort II Radio Bursts Detected by RSTN Throughout Photo voltaic Cycle 24, Photo voltaic Physics, Quantity 299, Concern 6, id.75. (2024) DOI:10.1007/s11207-024-02317-8