Current hypotheses counsel that each one life on Earth developed from a typical ancestor that diversified into the number of organisms seen at the moment. Scientists suggest that the eukaryotic department of this household tree shaped when two prokaryotes, an historical bacterium and archaeal cell, merged, forming a symbiotic relationship maintained over time.1
“If that is true,” mentioned Pedro Leão, an archaeal biologist at Radboud College, “we have now to know what forms of options this [archaeal] host was bringing to the primary eukaryote.” As a postdoctoral researcher in Brett Baker’s lab on the College of Texas at Austin, Leão explored the archaeal origins of eukaryotes, or eukaryogenesis.
Leão stumbled upon prokaryotic protection methods after he and his colleagues recognized archaea-infecting viruses.2 He reasoned that archaea, like micro organism, would additionally possess antiviral mechanisms, and these may have been preserved in trendy eukaryotes. He began digging into the literature in quest of info on archaeal protection methods and the origins of eukaryotic immunity, and got here throughout a perspective paper that piqued his curiosity: It attributed eukaryotic immune elements predominantly to micro organism and solely briefly talked about the existence of archaeal protection proteins.3
Leão realized that one motive for this archaeal slight was that archaeal genomes have been poorly represented within the research that investigated the prokaryotic origins of eukaryotic protection methods.4,5 “I used to be like, ‘Okay, that is a straightforward job for what we do. We are able to simply curate a very good dataset of archaea genomes and search for precisely the identical issues,’” Leão recalled.
He and his colleagues explored the archaeal protection methods of Asgard archaea, the closest trendy prokaryotic relative to eukaryotes, and in contrast their homology to these of eukaryotes. In a paper revealed in Nature Communications, the group demonstrated that two courses of protection system proteins present in these archaea are associated to these of eukaryotes.6 The findings provide deeper perception into the origins of early immune methods and the way they functioned.
Leão and his group used a database of prokaryotic protection methods to check the distribution of full methods within the genomes of archaea, together with Asgard archaea, and micro organism.7 The researchers recognized two teams of proteins that have been extra widespread in Asgard archaea than in different archaea and micro organism: argonautes, proteins from the RNA-induced silencing advanced, and viperins (quick for virus-inhibitory protein, endoplasmic reticulum-associated, interferon inducible).
Viperins and argonautes are each extremely represented in eukaryotic antiviral protection methods, so the group in contrast these proteins’ similarity to these present in Asgard archaea.8,9 They constructed a phylogenetic tree utilizing eukaryotic, archaeal, and bacterial genomes and confirmed that each viperin and argonaute proteins in eukaryotes shared an ancestor with these from Asgard archaea. They additional confirmed that the structural homology, together with key useful domains, of each proteins was preserved between archaea and eukaryotes.
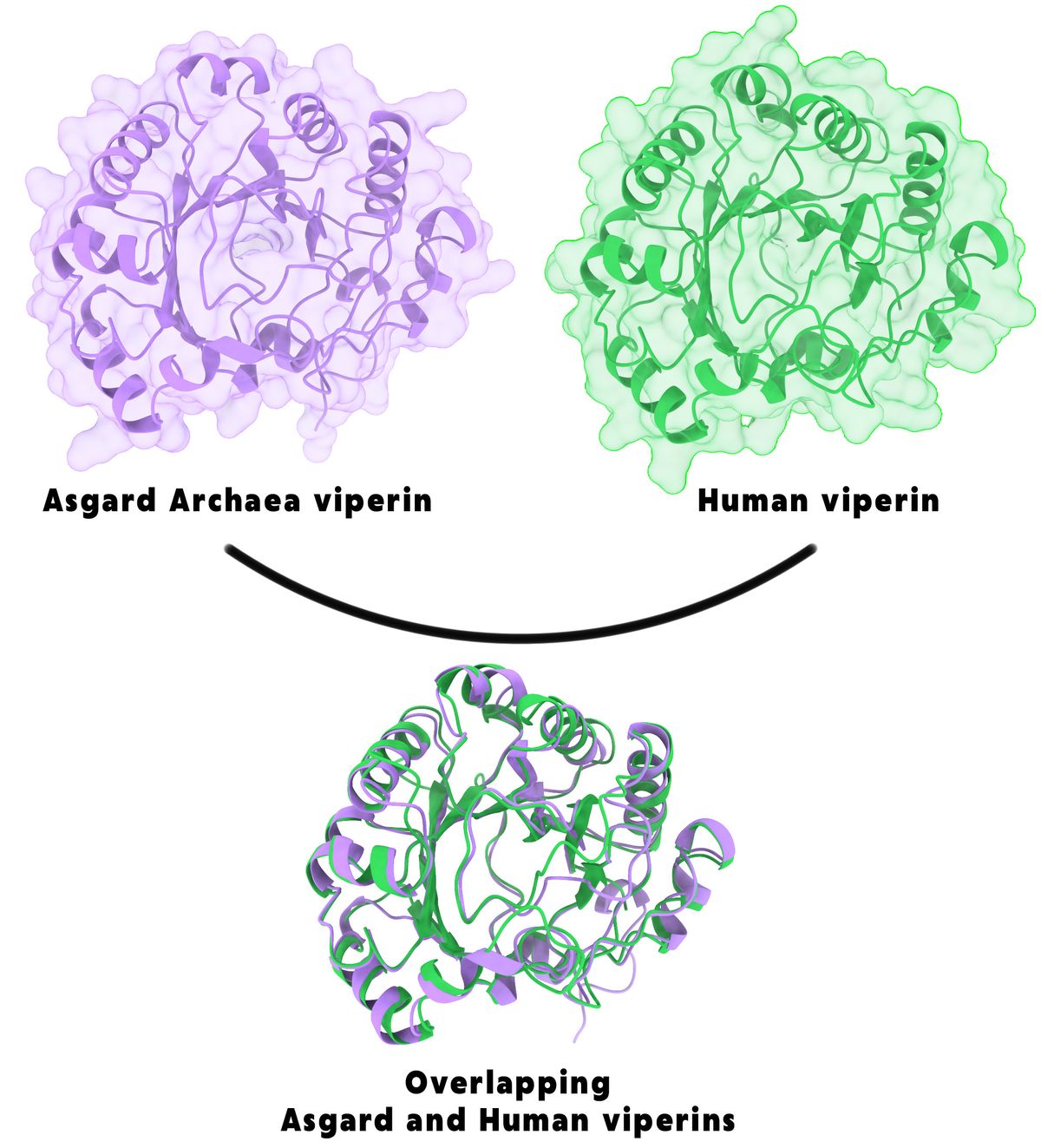
Researchers illustrated how protection proteins from a gaggle of Asgard archaea, the closest trendy prokaryotic relative to eukaryotes, is extremely just like the identical proteins present in people.
Pedro Leão
Whereas the shared sequence and construction homology of those proteins was promising, Leão sought to additional show that these archaeal proteins functioned like these of eukaryotes. The group expressed 48 totally different Asgard viperin genes in Escherichia coli earlier than introducing bacteriophages to guage the viperins exercise. Of the proteins produced, 9 protected E. coli in opposition to virus an infection. Since some sequences have been extra just like these of eukaryotes, the researchers optimized the viperin genes that encoded these 9 proteins for expression in E. coli, and one extra archaeal viperin demonstrated anti-phage exercise.
The group additionally discovered that, on common, Asgard archaea have a comparable variety of protection methods per genome to different archaea and micro organism. Nevertheless, some courses had a a lot decrease ratio, together with Heimdallarchaeia, which is most just like eukaryotes.
“In my thoughts, this can be a good tip that we would have some distinctive protection methods simply in archaea generally,” Leão mentioned. He intends to discover archaea-specific protection methods in additional element in his lab. “If we maintain searching for protection methods in Archaea by means of homologs of already described ones in micro organism, we can’t discover them.”
Buzz Baum, a cell biologist learning archaea on the Medical Analysis Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology who was not concerned within the research, shared this thought. “There is likely to be a number of issues in Asgard which we do not know what they do, however really do perform in [an] immune context.” He’s additionally excited to be taught extra about how the archaeal immune system features. “It will likely be fantastic within the coming years to have the ability to see, in actual time, how cells make use of these methods to defend themselves.”