Think about a busy espresso store the place a single barista has to deal with a number of prospects directly. In a conventional setup, the barista would take one order, put together the drink, and solely then transfer on to the subsequent buyer—inflicting lengthy wait instances. However what if the barista may take a number of orders, put together drinks in parallel, and notify prospects when their orders are prepared? That’s precisely how Node.js’s event-driven structure revolutionises server-side growth, making it extremely scalable and environment friendly.
Let’s dive into how Node.js handles 1000’s of concurrent connections with out breaking a sweat!
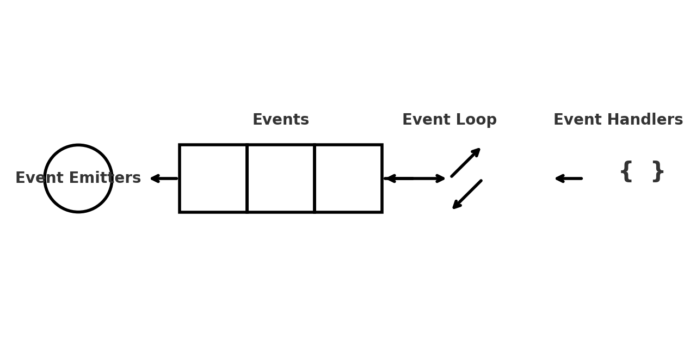
The Secret Sauce: The Single-Threaded Occasion Loop
Most conventional server fashions (like Apache or PHP-based servers) create a new thread for each incoming request. This strategy works high-quality for small-scale purposes however struggles when 1000’s of customers attempt to join concurrently.
Node.js, however, runs on a single-threaded occasion loop that processes a number of requests asynchronously. As an alternative of ready for a job (like studying a file or fetching knowledge from a database) to complete earlier than transferring on, Node.js registers a callback and retains dealing with different requests within the meantime.
Why does this matter?
- It reduces the overhead of making and managing a number of threads.
- It permits dealing with 1000’s of requests with minimal useful resource utilization.
- It eliminates context-switching delays present in multi-threaded architectures.
Comparability: Conventional Thread-Primarily based Mannequin vs. Node.js Occasion Loop
| Function | Conventional (Thread-Primarily based) Servers | Node.js (Occasion-Pushed) |
| Request Dealing with | Creates a brand new thread per request | Makes use of a single-threaded occasion loop |
| Reminiscence Utilization | Excessive (every thread consumes reminiscence) | Low (shared occasion loop) |
| Context Switching | Frequent, inflicting CPU overhead | Minimal, since there’s one principal thread |
| Efficiency Underneath Load | Degrades with extra connections | Scales effectively with minimal sources |
Actual-World Analogy: Consider it like a restaurant with waiters (threads) dealing with every desk individually vs. a self-service system the place prospects (requests) place orders, and the system notifies them when their meals (response) is prepared.
Asynchronous Processing: The Spine of Node.js’s Efficiency
On the core of Node.js’s effectivity is its non-blocking I/O mechanism.
How It Works:
- A request (like fetching consumer knowledge from a database) is available in.
- As an alternative of ready for the info, Node.js delegates the duty and strikes on.
- When the database responds, Node.js processes the info and returns it to the consumer.
This ensures the server stays responsive even underneath heavy hundreds.
Occasion-Pushed Programming & The Energy of Occasions
Node.js purposes are designed round occasions—very similar to how notifications work on a smartphone. When an occasion happens (e.g., new knowledge arrives), it triggers a callback operate, preserving the system extremely environment friendly.
Scalability in Motion: The place Node.js Shines
1. Dealing with 1000’s of Concurrent Connections
Many purposes at this time—social media platforms, streaming companies, or real-time dashboards—take care of excessive consumer visitors. Conventional servers would possibly crash underneath this load, however Node.js effortlessly handles 1000’s of concurrent customers.
Finest for: Chat apps, collaborative instruments, multiplayer video games
2. Actual-Time Purposes & Prompt Occasion Processing
Node.js’s event-driven mannequin makes it excellent for real-time purposes. As an alternative of regularly checking for updates (polling), the system reacts solely when crucial—optimizing efficiency.
Finest for: Stay notifications, inventory market dashboards, IoT gadgets
3. Microservices & Distributed Programs
Node.js aligns completely with microservices structure, the place a number of small companies deal with totally different duties independently. These companies talk asynchronously utilizing event-driven mechanisms, making certain seamless scaling.
Finest for: Enterprise purposes, e-commerce platforms, cloud-based programs
Avoiding Pitfalls: Optimizing Node.js for Scalability
1. Keep away from Blocking the Occasion Loop
Since Node.js runs on a single thread, CPU-heavy operations can block execution, resulting in gradual response instances.
Answer: Offload intensive duties to Employee Threads or separate companies.
2. Use a Load Balancer & Clustering
By default, Node.js runs on a single CPU core. To scale effectively:
- Use the Cluster Module to create a number of employee processes.
- Deploy behind a load balancer (e.g., NGINX) to distribute visitors.
3. Leverage Message Brokers for Scaling
For giant-scale purposes, integrating with message brokers like RabbitMQ or Apache Kafka helps queue requests effectively—stopping server overload.
Last Ideas: Why Node.js is Constructed for the Future
With its event-driven structure, non-blocking I/O, and scalability-first design, Node.js continues to energy among the world’s largest purposes. From real-time messaging platforms to high-performance APIs, its means to deal with huge visitors with minimal sources makes it a go-to selection for contemporary builders.
Wanting Forward
As demand for extremely responsive, scalable purposes grows, Node.js’s strategy ensures builders can construct for the long run—with out worrying about efficiency bottlenecks.