Each breath you absorb a polluted metropolis delivers one thing greater than oxygen. Laced by the air are particles so high quality they float for days, particles smaller than a bacterium that may journey deep into lung tissue, slip into the bloodstream, and, mounting proof suggests, work their means by into the mind itself. Now, a research of virtually 28 million older People has pushed that proof additional nonetheless, discovering that long-term publicity to this high quality particulate air pollution raises the chance of Alzheimer’s illness by mechanisms that seem to behave straight on the mind, bypassing the standard suspects of coronary heart illness, hypertension, and despair.
The discovering issues for a easy cause: Alzheimer’s illness has no treatment. It impacts round 57 million folks worldwide, a quantity anticipated to triple by 2050, and the one actual hope of stemming that tide lies in figuring out dangers we would really do one thing about. Air high quality, in contrast to age or genetics, is certainly one of them.
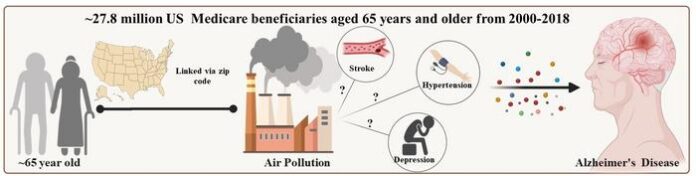
The research, led by Yanling Deng at Emory College’s Rollins College of Public Well being and printed in PLOS Drugs, drew on Medicare claims knowledge spanning almost 20 years. The researchers tracked who developed Alzheimer’s and what the air round their properties had contained within the previous 5 years, rigorously mapping concentrations of PM2.5, the high quality particles on the centre of concern, to every participant’s zip code at one-kilometre decision. Of the 27.8 million folks within the cohort, roughly 3 million went on to develop Alzheimer’s. Every step up the air pollution ladder, measured in increments of three.8 micrograms per cubic metre of air, was related to an 8.5 per cent enhance in Alzheimer’s threat. That relationship held after accounting for dozens of variables, from revenue and training ranges to smoking charges and physique mass index throughout counties.
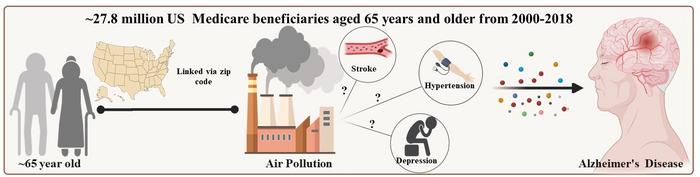
None of that can shock researchers already monitoring the PM2.5 and dementia literature. What the Emory staff got down to resolve was a deeper query: how does air pollution really do that? The apparent candidates had been the persistent illnesses that path soiled air wherever it settles, hypertension, stroke, and despair, circumstances recognized to lift Alzheimer’s threat in their very own proper. If these had been the first pathway, cleansing up air would nonetheless assist, however largely by stopping these intermediate circumstances first.
The mediation evaluation that Deng’s staff ran informed a unique story. Once they formally examined how a lot of the pollution-Alzheimer’s hyperlink ran by hypertension, stroke, or despair, the numbers had been strikingly small. Hypertension accounted for simply 1.6 per cent of the affiliation. Melancholy for two.1 per cent. Stroke, essentially the most vascular of the three, for 4.2 per cent. The remaining 90-odd per cent appeared to bypass these intermediaries completely. Because the authors put it, long-term publicity to high quality particulate air air pollution was related to the next threat of Alzheimer’s illness “largely by direct results on the mind relatively than by frequent persistent circumstances comparable to hypertension, stroke, or despair.”
That phrase, direct results on the mind, factors in the direction of mechanisms nonetheless being labored out however now not completely speculative. PM2.5 particles, and the inflammatory indicators they carry, can cross the blood-brain barrier. As soon as inside, they seem to advertise neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, and in kids and younger adults residing in closely polluted cities, autopsy research have already discovered the early protein deposits, amyloid-beta plaques, tau tangles, the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s, years or many years earlier than they’d be anticipated to seem. The implication is uncomfortable: air pollution could start setting the stage for dementia lengthy earlier than any signs floor.
One subset of individuals confirmed a meaningfully totally different sample. Individuals who had already suffered a stroke carried a modestly however considerably elevated sensitivity to air pollution’s results on their Alzheimer’s threat. The place the broader inhabitants confirmed an 8.5 per cent enhance per publicity increment, stroke survivors confirmed nearer to 10.5 per cent. The Wald take a look at confirmed the interplay was not a statistical fluke. The authors recommend the explanation lies in what stroke does to the mind’s defences. A stroke can compromise the blood-brain barrier, the tight mobile seal that usually prevents giant molecules and particles from coming into neural tissue. With that barrier weakened, PM2.5 particles or their inflammatory messengers could penetrate extra simply, worsening the neuroinflammation and amyloid accumulation that drive Alzheimer’s pathology. “People with a historical past of stroke could also be significantly susceptible to the dangerous results of air air pollution on mind well being,” the authors write, calling it “an essential intersection between environmental and vascular threat elements.”
The dimensions of the dataset supplies a stage of statistical confidence that smaller European research, working with hundreds relatively than hundreds of thousands of individuals, couldn’t match. Earlier work from Swedish cohorts had recommended heart problems may mediate as a lot as half the pollution-Alzheimer’s affiliation. However these estimates, because the Emory staff notice, had been based mostly on analyses that didn’t correctly account for interactions between the air pollution publicity and the mediating circumstances themselves. When related research corrected for these interactions, their mediation estimates shrank dramatically, in the direction of figures a lot nearer to what this new evaluation discovered.
Limitations stay. Air pollution publicity was estimated at zip-code stage relatively than particular person addresses, and indoor sources comparable to cooking and heating weren’t captured. The research inhabitants skews in the direction of white, fee-for-service Medicare enrolees, so generalisability to different teams requires warning. And the five-year publicity window, although chosen intentionally, can’t seize what occurred in individuals’ lungs and brains throughout earlier many years of life.
However the coverage logic the findings help is easy. Lowering ambient PM2.5 concentrations seems more likely to cut back Alzheimer’s incidence by pathways that cardiovascular remedy alone can’t deal with. In a illness with no efficient remedy, that could be among the many most actionable levers accessible. For the one in 5 People who’ve survived a stroke, the implication is sharper nonetheless: the air exterior their window shouldn’t be a impartial backdrop, however one thing extra actively working towards the mind tissue they’ve left.
Examine hyperlink: https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004912
If our reporting has knowledgeable or impressed you, please think about making a donation. Each contribution, irrespective of the dimensions, empowers us to proceed delivering correct, participating, and reliable science and medical information. Thanks for standing with us!