In 1997, two unbiased analysis teams printed their discovering that the enlargement of the universe is accelerating. The idea of “darkish vitality” was launched as a hypothetical supply of destructive gravity, which might add the acceleration to the usual Large Bang mannequin. Subir Sarkar now claims that the 2 teams made the error of trying solely at one patch of the sky, and that when the entire sky is taken into account, there is no such thing as a proof for acceleration, therefore no want for “darkish vitality”.
(You shouldn’t consider us as the middle of this enlargement. Suppose as an alternative that we’re a raisin in a loaf of raisin bread baking within the oven. Because the bread rises, each raisin is transferring away from each different raisin. The additional the space between two raisins, the quicker they’re transferring aside.)
Within the Large Bang idea, the enlargement was “baked into” the universe from the very starting. Issues which might be distant are distant as a result of their preliminary velocity was very totally different from our personal. Issues which might be shut by had velocities near ours, so that they by no means bought very removed from us, even after 13 billion years.
This image is modified by gravity. All matter that we all know of has optimistic gravitational attraction, so the enlargement of the universe must be progressively slowing down.
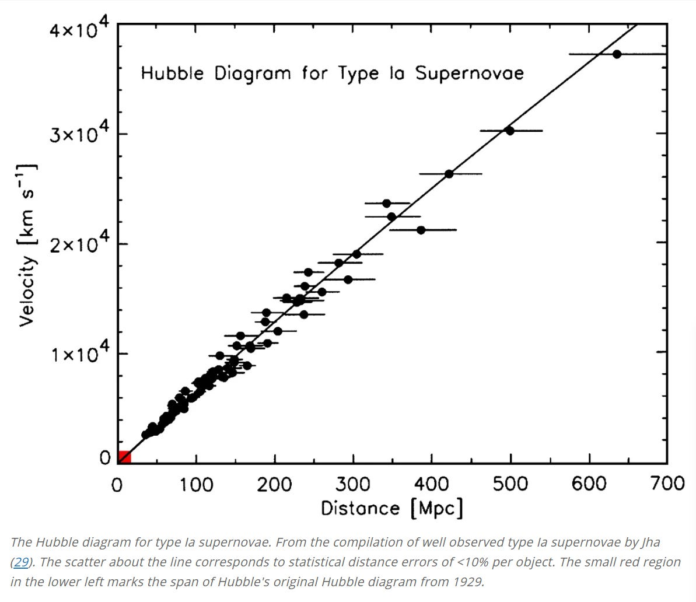
The enlargement of the universe is charted by evaluating the recessional velocity to the space from us.
Because it seems, the recessional velocity is straightforward to measure. All the weather emit mild at attribute colours (wavelengths) which might be very properly outlined. For instance, hydrogen emits a few of its mild as a particular shade of inexperienced. When a galaxy is transferring quickly away from us, that inexperienced would possibly seem yellow due to its movement. That is known as the “redshift” as a result of the colour is shifted towards the purple finish of the spectrum.
In Hubble’s Legislation, a galaxy’s redshift is proportional to its distance away from us. However how is the space decided? Hubble did the only factor and assumed that the faint, small galaxies have been additional away and the big, shiny galaxies have been nearer.
However at present, we attempt to do higher than Hubble. If a galaxy seems small and dim, it could be as a result of it’s removed from us, or it’d simply be a small, dim galaxy that’s shut by. How can we inform? In figuring out the space/velocity relationship, it’s distance that may be a lot tougher to find out.
The easiest way we’ve discovered thus far includes supernovae. A supernova is an exploding star. Over a number of weeks, a star on the finish of its life turns into phenomenally shiny, billions of instances brighter than it was whereas it was simply buzzing alongside like our solar. However straightforward come — straightforward go; the brightness fades quickly. Tracing the rise and fall of sunshine from supernovae in distant galaxies is how astronomers decide how distant they’re.
Astronomers communicate of “commonplace candles”. What they imply is that they know the way shiny a supernova is on an absolute scale, to allow them to infer its distance from how shiny it seems to be. Supernovae make good “commonplace candles” as a result of (1) they’re super-bright, so we are able to see them even when they’re very distant; that method, we are able to discover the universe far again in time. (2) we are able to calculate absolutely the brightness from how quickly they explode, utilizing an empirical relationship found by Mark Phillips. Again in 1993, Phillips charted the brightness of simply 9 close by supernovae for which we have been assured of their distance from earth, and which we have been lucky sufficient to have caught early on, so we had data of their waxing time. He confirmed that from the rise time of the sunshine curve (what number of days from preliminary explosion to most) you may calculate absolutely the brightness fairly precisely.
So the undertaking through the Nineteen Nineties was to maintain an eye fixed out for supernova explosions in distant galaxies. They watched the brightness wax from night time to nighttime, to see how quickly it reached its peak brightness. From this time scale, they have been in a position to decide how shiny the supernova would seem if it have been shut by. They in contrast that to how shiny it seems and inferred a distance.
Hubble’s legislation says that the recessional velocity of an object is proportional to its distance away from us.
Add to this image the truth that galaxies have mass and they’re pulling on one another, barely slowing the enlargement over time. The objects which might be furthest away are seen as they have been lengthy, way back, as a result of it has taken their mild so lengthy to succeed in us. So they are going to now be going considerably slower than we observe them. Compared, mild from objects which might be shut didn’t take so lengthy to succeed in us, so we see them just about with the velocities they’ve at current.
So we anticipate that the galaxies which might be furthest away will deviate from the straight line in Hubble’s Legislation. Their velocities will seem a little bit too massive, as a result of we see them as they have been way back (quicker) not as they’re now (slower). The straight line ought to bend barely upward on the far finish.
The graph above represents solely 15% of the historical past of the universe. Suppose we have been to increase it again to 50% of the universe. We’d hope to see that bending upward. This was the undertaking of astronomy within the final decade of the twentieth century, when telescopes had superior to the purpose the place we might see far-away objects.
However shock! What astronomers discovered as an alternative was that the curve bends downward for supernovae which might be very distant. It’s as if gravity is working in reverse, pushing as an alternative of pulling.
Physicists had no actual rationalization for the acceleration, or the “destructive gravity”. They added the phenomenon to their Large Bang fashions and known as the offender “darkish vitality”, however they didn’t have any understanding of what darkish vitality is or why it ought to have this distinctive property of “destructive gravity”.

Our galaxy is near Andromeda galaxy, and a number of other different massive objects in that route. Because of this, we’re being pulled within the Andromeda route. It occurs that that is the route the place many of the supernovae have been discovered on which the calculations have been primarily based that led to the accelerating enlargement and the 2011 Nobel prize. The Hubble curves that have been calculated did not take account of our personal galaxy’s movement. When that is correctly taken into consideration, the acceleration disappears.
Our personal movement makes the close by galaxies seem like transferring a little bit quicker than they’d be in any other case. Essentially the most distant galaxies seem, as compared, to be transferring a little bit slower than they need to be, not as a result of they’re actually too gradual however as a result of we’re evaluating to the anomalous velocity measurements of close by galaxies. This accounts for the downward curve of the Hubble graph. Essentially the most distant galaxies, far again in time, aren’t actually transferring slower than we might anticipate; therefore there is no such thing as a proof that they’ve been accelerating within the interim. With out proof of acceleration, there is no such thing as a want for darkish vitality.
The very best methodology we have now for judging distance of a supernova is to make use of the empirical relationship with waxing time to deduce absolute brightness, then evaluate that to the obvious brightness to calculate its distance. In accordance with Sarkar, the Joint Lightcurve Evaluation workforce [Ruben & Hayden, 2016] didn’t do that. They included an additional fudge issue, by which the connection between waxing time and brightness relies upon immediately on distance! If that is what they did, it’s really a breach of experimental protocol. The supernova is not a “commonplace candle”, and the info can say something you need them to say, relying on the way you modify the fudge issue.
Sarkar’s story, if appropriate, removes one massive anomaly from the Large Bang idea, and makes for a greater match between idea and what we all know. However there stay two different anomalies that hang-out the Large Bang, and which might doubtlessly deliver the idea down. Briefly, these are
- We don’t perceive what the gravitating mass within the universe comes from. We suspect it isn’t unusual electrons, neutrons, and protons, as a result of if it have been, accounts of the First Three Minutes would lead to much more helium and particularly lithium and deuterium.
- Latest outcomes from the Webb Area Telescope point out that there have been unusual stars and galaxies virtually instantly after the Large Bang. Our fashions can’t account for how they could have appeared so quick.
I wrote about each of those (along with darkish vitality) final 12 months.
I don’t assume the narrative of the Large Bang will survive despite the fact that it has dominated the sector of astronomy all by means of my skilled life. Time will inform.