Photo voltaic kind V radio bursts are broad-band continua related to kind III bursts, that are usually believed to be attributable to coronal electron beams. Sort V bursts seem generally for 0.2 to three minutes as a continuum following an intense kind III burst or group of bursts.
The spectral peak of kind V bursts is usually beneath 100 MHz. The high-frequency edge is beneath the beginning frequency of the related kind III burst, and the low-frequency restrict is commonly lower than that of ground-based spectrometers (20 – 40 MHz). Each beginning and trailing edges drift normally however not at all times from excessive to low frequencies. Thus, the mix of a kind V and III burst has the form of a flag on a pole within the spectrogram. Stewart (1978) studies that kind III/V bursts are higher correlated with arduous X-ray flares than single kind III bursts (80% vs. 20%), suggesting extra highly effective occasions. In some circumstances, there’s a time hole between the kind III burst and the beginning of the kind V emission. Such circumstances are known as indifferent occasions. The round polarization of kind V bursts is weak (of order 10% or much less). Dulk, Gary, and Suzuki (1980) report that it’s normally reversed in comparison with the previous kind III burst.
Electron beams are two-stream unstable and drive Langmuir waves that couple into radio waves (kind III burst). Within the non-linear part, the electron distribution turns into quasi-stationary and elongated in ahead route. This distribution has been predicted to be unstable in the direction of the electron firehose instability involving resonant protons and for giant anisotropies additionally resonant electrons (Pilipp and Benz 1977). The secondary instability then scatters the beam electrons into transverse route. It could be speculated that the isotropic electrons develop a loss-cone by precipitation and turn into unstable to masering radio emission.
Che et al. (2014) have simulated the non-linear evolution of electrons beams by particles-in-cell (PIC) and located proof for the sequence of instabilities resulting in kind III radio emission and scattering. After an early part dominated by rising Langmuir waves, the electron two-stream instability drives non-propagating Weibel-like waves that excite each kinetic Alfvén waves and whistler waves by wave–wave coupling. These kinetic processes scatter beam electrons into transverse route.
Right here we current a rare kind V occasion and ask the query: Can all of this kind III/V occasion be defined by phenomena originating from the non-linear evolution of the two-stream instability?
Observations
The flare SOL2021-05-07T03:39 was chosen for its mixture of a meter wave kind U burst adopted by a kind V burst. The occasion was noticed by a number of stations of the e-CALLISTO community. We used the info from ASSA in Sunnydale (Australia). The spectrometer was programmed to watch the frequency vary 15 – 87 MHz with a decision of 0.375 MHz. Calibration is just not obtainable.
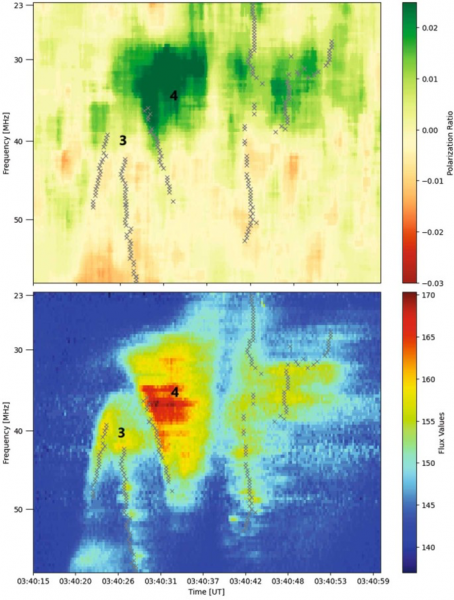
Determine 1 exhibits an summary of the radio emission. The background was decided in time intervals of low fluctuations throughout half-hour earlier than and after the bursts. The 5%-quantile of the flux was used as background and subtracted.
The buildings of the emission within the spectrogram are characterised by their peak flux in time. The height time is set from Gaussian suits at every frequency. The very best peak at every frequency is chosen, and its peak time is recorded. The values outline a curve within the spectrogram (ν,t)-space). Outcomes are proven in Determine 1 (backside) and utilized in Determine 1 (prime) to establish buildings.
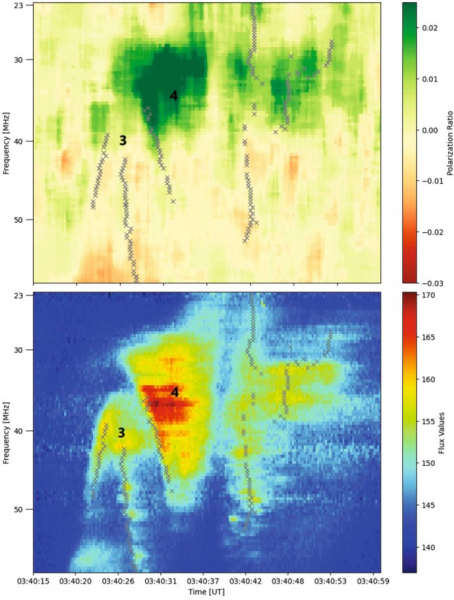
Determine 1: Backside: Spectrogram exhibiting radio flux with U burst (occasion 3) and kind V burst (occasion 4) in uncalibrated items. Black crosses “x” mark an area most of the flux in time for kind III und U bursts. For the kind V emission, the “x” signifies the start line of the emission at a given frequency. High: Ratio between left and proper round polarization.
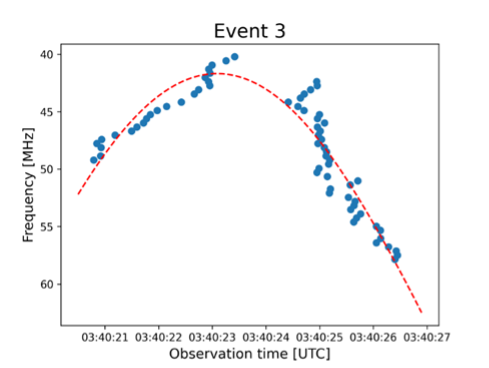
Determine 2: U Burst: Blue dots: peak instances in frequency channel. Crimson-dashed curves: fitted to peak.
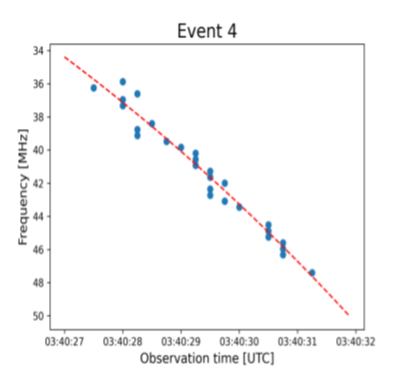
Determine 3: Sort V: Blue dots point out instances of 8% enhance above background. Crimson-dashed curves: fitted to beginning edge.
Outcomes and Dialogue
- Drift fee
The drift of the descending department of the U-burst is -0.30 [s-1]. For a density scale peak of 1010cm (2 MK) and plasma emission, the beam velocity is 6·109 cm/s. The beginning fringe of the kind V burst drifts with -0.15 [s-1]. If the emission course of is plasma emission, the drift velocity of the kind V beginning edge is half of that of the U-burst. If the emission is electron cyclotron maser and the magnetic scale peak is identical because the density scale peak, the speed is 1/4 of the U-burst beam. For each circumstances of emission, the info counsel that the Sort V inflicting electrons have decrease velocity than the kind III inflicting electrons.
- Begin of occasions
The beginning fringe of the kind V emission begins at about 03:40:23 UTC, coinciding with the
loop apex of the U-burst. Thus the kind V emission begins when the electron beam passes the apex of the loop.
- Round Polarization
Determine 1 prime signifies that the polarization of the kind U burst is appropriate with zero,
The polarization of the kind V burst, nonetheless, is left round (inexperienced). Thus the kind III and kind V emissions could also be attributable to totally different mechanisms.
Situation and Conclusions
The info of the U burst (Occasion 3) and kind V burst (Occasion 4) might be mixed right into a
coherent situation:
- Electrons are accelerated close to the footpoints of a magnetic loop. A beam of electrons propagates alongside a coronal loop.
- The beam is two-stream unstable, thrilling Langmuir waves. They collapse within the nonlinear part thrilling ion acoustic waves. Wave-wave coupling produces radio emission, which is noticed as kind III und U bursts.
- The speed distribution of a beam is preferentially parallel, driving the electron Firehose instability. Within the nonlinear part, it corresponds to thrilling Weibel and whistler waves, which scatter energetic electrons into perpendicular velocity. The non-thermal electrons kind an isotropic halo.
- After the beam has handed, the quasi-isotropic electron distribution deforms, dropping electrons in parallel route that escape and precipitate.
- The energetic electrons develop a loss-cone distribution. It turns into unstable to electron maser emission, and causes a kind V radio emission at frequencies above the plasma frequency.
This situation suggests a fancy interaction of assorted kinetic plasma processes.
PIC simulations have been inspiring, however are too restricted but to substantiate the situation.
Extra imaging observations of the spatial relation between III/U and V bursts are additionally vital.
Based mostly on the latest paper: Benz, A.O., ·Huber, C.R., Timmel, V., Monstein, C. Commentary of an Extraordinary Sort V Photo voltaic Radio Burst: Nonlinear Evolution of the Electron Two-Stream Instability: Photo voltaic Physics, 299, 146 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-024-02395-8
References
Che, H., Goldstein, M. L., Vinas, A. F. 2014, Phys. Rev. Lett., 112, 061101.
Dulk, G.A., Gary, D.E., Suzuki, S. 1980, A&A, 88, 218.
Pilipp, W.G., Benz A.O. 1977, A&A, 56, 39.
Stewart R.T. 1978, Photo voltaic Phys,. 58, 121.