Density fluctuations populating the heliosphere intrude with propagating radio photons, altering their trajectories by way of frequency-dependent results like scattering. Crucially, these density fluctuations are anisotropic, resulting in anisotropic scattering and directional radio-wave propagation. Which means that observers at completely different positions could receive completely different estimations of radio properties. Such results are notably evident in photo voltaic radio bursts that are emitted by way of the plasma emission mechanism. It has been proven that detectors at varied places will measure vastly completely different radio burst properties, together with the flux (which may range by orders-of-magnitude), supply sizes, and supply positions (Kontar et al. 2019, Kuznetsov et al. 2020, Musset et al. 2021). Nevertheless, till not too long ago, it was unknown whether or not the measured decay and rise instances of photo voltaic radio bursts additionally range with the observer’s location. Decay instances are of specific curiosity since they’re dominated by scattering results, and have thus been used to approximate the extent of small-scale density fluctuations within the heliosphere (e.g. Krupar et al. 2020). Chrysaphi et al. (2024) handle this open query utilizing stereoscopic observations of Sort III photo voltaic radio bursts from 4 non-collinear, angularly-separated spacecraft: Photo voltaic Orbiter (SolO), Parker Photo voltaic Probe (PSP), STEREO-A (STA), and WIND.
Methodology & Outcomes
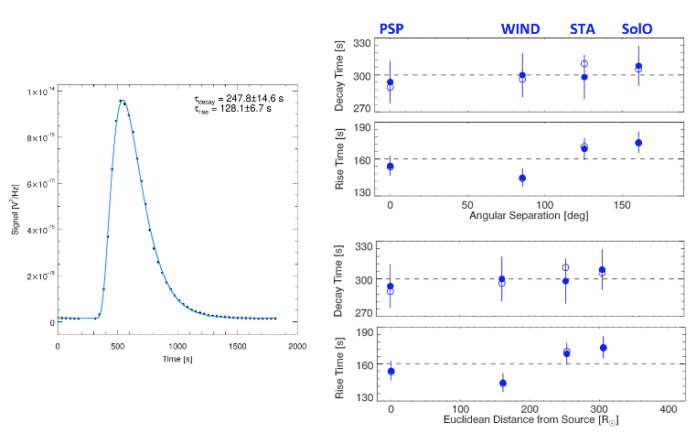
Every Sort III burst is concurrently noticed (at comparable frequencies) by a minimum of 3 spacecraft at completely different vantage factors. The radio mild curves are match with a single perform that may describe the whole thing of the sign (Determine 1), permitting for improved estimations of the decay time and enabling a simultaneous estimation of the rise time and peak time/amplitude. The reliability of the proposed perform can also be illustrated, notably compared to the normally-favoured single-exponential match to the decay section. By efficiently becoming the whole thing of noticed radio mild curves with the proposed perform, Chrysaphi et al. (2024) display that the rise section of radio bursts is non-exponential, rising at a non-constant charge. As a substitute, the rise section’s development charge is a perform of time, initially rising quicker than an exponential.
The angular separation between the spacecraft and the radio supply is calculated contemplating the 3D positions of the spacecraft (and never merely their longitudinal positions), additional permitting for an estimation of the Euclidean separation between the spacecraft and the supply (as a substitute of merely evaluating their heliocentric distances). Subsequently, any dependence of measured rise and decay instances is examined by way of each the angular and Euclidean separations between the supply and spacecraft. Chrysaphi et al. (2024) discover that the rise and decay instances don’t range with the place of the observer (whether or not the variation is angular or Euclidean; Determine 1). Subsequently, rise and decay instances are recognized as the one radio burst properties whose measurements stay impartial of the observer’s vantage level.
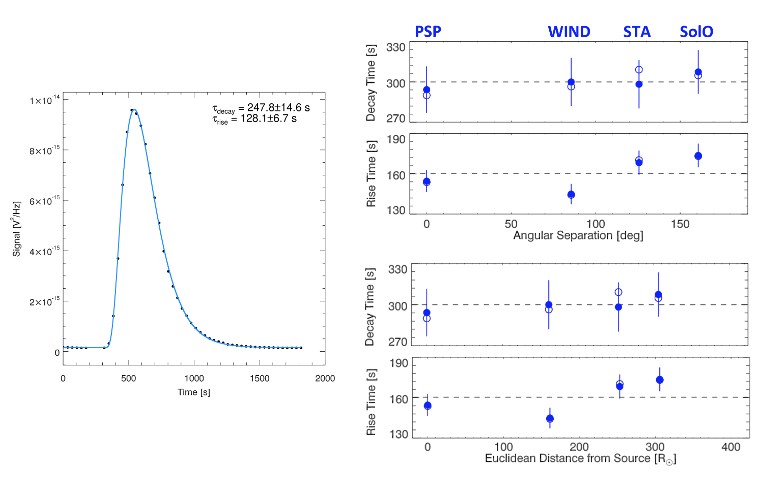
Determine 1. Left: Mild curve of a Sort III photo voltaic radio burst recorded by a spacecraft (black datapoints) being slot in its entirety with the proposed perform (blue curve). Proper: Measurements of the decay and rise instances as a perform of the angular separation (prime) and the Euclidean distance (backside) between the spacecraft and the radio supply. Determine tailored from Chrysaphi et al. (2024).
The frequency dependence of the rise and decay instances of radio bursts can also be examined (Determine 2). Greater than 300 mild curves are analysed, protecting frequencies (f) from 60 – 1725 kHz. Each the rise and decay instances are discovered to have an roughly 1/f relation, as has been beforehand proven for decay instances (Kontar et al. 2019). Moreover, Chrysaphi et al. (2024) discover that the ratio of rise-to-decay instances is impartial of the frequency (Determine 2). This result’s in contrast in opposition to rise-to-decay time ratios calculated utilizing already-available knowledge, total protecting 4 many years of frequencies starting from 0.06 – 130 MHz, confirming the obtained frequency independence. On condition that decay instances are considerably affected by the (frequency-dependent) scattering results, this discovering implies that rise instances are affected by scattering results in a proportionate method. This gives proof that scattering not solely impacts the decay section, however can also be an necessary contributor to the rise section of photo voltaic radio bursts.
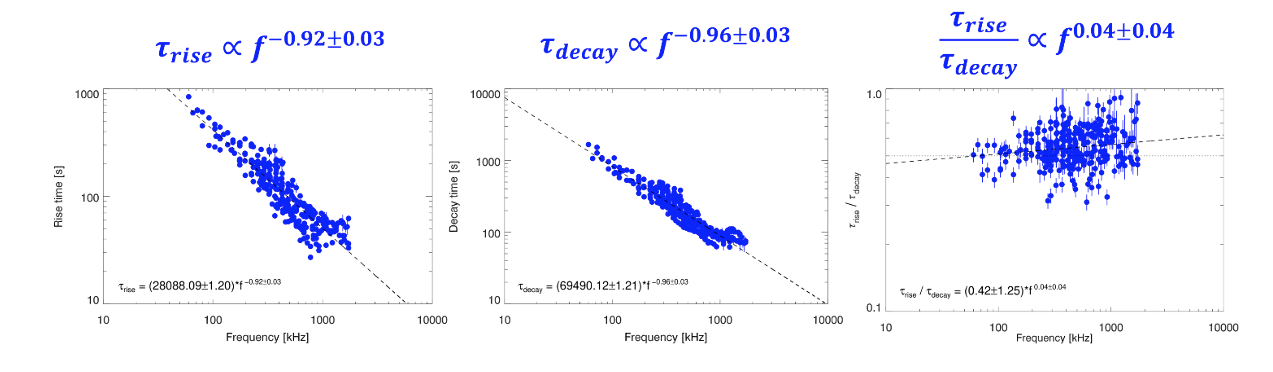
Determine 2. Measurements of the rise time (left), decay time (center), and the rise-to-decay time ratio (proper) as a perform of the noticed frequency. Determine tailored from Chrysaphi et al. (2024).
Conclusions
- Rise and decay time measurements of photo voltaic radio bursts rely upon neither the angular nor the Euclidean separation of the detector from the radio supply.
- The rise-to-decay time ratio is impartial of frequency, indicating that the rise section of photo voltaic radio bursts is affected by scattering in a proportional method to their decay section. Subsequently, scattering results are recognized as a big contributor to the rise section, including to our understanding of the plasma emission course of.
- The rise section of photo voltaic radio bursts grows at a non-constant, non-exponential charge.
- Capabilities that efficiently match the whole thing of the radio burst mild curves ought to be used for dependable estimations of the rise and decay instances.
Primarily based on a latest paper by Nicolina Chrysaphi, Milan Maksimovic, Edurard P. Kontar, Antonio Vecchio, Xingyao Chen, and Aikaterini Pesini. First dedication of the angular dependence of rise and decay instances of photo voltaic radio bursts utilizing multi-spacecraft observations. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 687, L12 (2024). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202348175
References
Kontar, E. P., Chen, X., Chrysaphi, N., et al. 2019, ApJ, 884, 122
Krupar, V., Szabo, A., Maksimovic, M., et al. 2020, ApJS, 246, 57
Kuznetsov, A. A., Chrysaphi, N., Kontar, E. P., et al. 2020, ApJ, 898, 94
Musset, S., Maksimovic, M., Kontar, E. P., et al. 2021, A&A, 656, A34